Java is one of the most popular programming languages, and a large part of its strength comes from its rich set of APIs, particularly the Java Collections Framework (JCF). The JCF provides a set of classes and interfaces that allow developers to manage groups of objects effectively. Whether you're dealing with simple lists, complex maps, or custom data structures, the JCF provides a standardized way to work with these elements.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the key components of the Java Collections Framework, provide real-life examples to explain how they work, and discuss best practices along with some advanced features.
1. What Is the Java Collections Framework?
The Java Collections Framework is essentially a collection of pre-built data structures (like lists, sets, and maps) and algorithms that provide common ways to organize and manipulate data. Imagine you are managing an online retail store; you’ll have to deal with lists of customers, orders, and products. The JCF provides an efficient, tested, and standardized way to manage such collections.
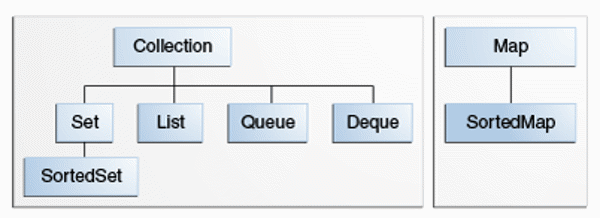
2. Core Components of the Java Collections Framework
The JCF includes a few major components:
a. List
A List is an ordered collection of elements. A real-life example would be a shopping cart where items are added sequentially. The order in which you add items is preserved, and you can add or remove items by their index.
- Common Implementations:
ArrayList: Backed by a dynamic array, it’s fast for random access but slower for inserting elements in the middle of the list.LinkedList: Implemented as a doubly-linked list, it’s slower for random access but efficient for insertions and deletions in the middle of the list.- Example Code:
java
List<String> shoppingCart = new ArrayList<>();
shoppingCart.add("Apple");
shoppingCart.add("Banana");
shoppingCart.add("Orange");
System.out.println("Shopping Cart: " + shoppingCart);
Real-life analogy: Think of an assembly line where items are added one after another. If you need to access or remove items, you can simply refer to their position.
b. Set
A Set is a collection that doesn’t allow duplicate elements. Think of it like attendees at a concert—you only want to count unique people, even if they try to enter twice.
- Common Implementations:
HashSet: The most commonly used set, backed by a hash table. It offers constant time performance for basic operations but doesn't maintain order.TreeSet: Maintains a sorted order of elements, but comes with a performance cost compared toHashSet.- Example Code:
java
Set<String> attendees = new HashSet<>();
attendees.add("Alice");
attendees.add("Bob");
attendees.add("Alice"); // This will not be added
System.out.println("Unique Attendees: " + attendees);
c. Map
A Map is a collection that associates keys with values. It’s like a contact list on your phone, where each name (key) maps to a phone number (value).
- Common Implementations:
HashMap: The most widely used implementation, providing constant time for basic operations but doesn't maintain order.TreeMap: LikeTreeSet, it maintains a sorted order of its keys.- Example Code:
java
Map<String, String> phoneBook = new HashMap<>();
phoneBook.put("Alice", "123-456-7890");
phoneBook.put("Bob", "987-654-3210");
System.out.println("Bob's Number: " + phoneBook.get("Bob"));
3. Best Practices for Java Collections Framework
To use the Java Collections Framework efficiently, here are some best practices:
a. Use the Right Collection Type
Pick the right collection type based on the scenario:
- Use a
Listif order matters. - Use a
Setif you want unique elements. - Use a
Mapif you need key-value associations.
b. Avoid Raw Types
Always use generics to ensure type safety.
- Bad Practice:
java List items = new ArrayList(); // Raw Type
- Good Practice:
java List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
c. Prefer Interfaces over Concrete Implementations
Always declare variables using collection interfaces (List, Set, Map) rather than the concrete class (ArrayList, HashSet).
- Good Practice:
java List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
d. Use Concurrent Collections for Multi-threading
If working in a multi-threaded environment, prefer collections from the java.util.concurrent package, such as ConcurrentHashMap.
4. Advanced Features of Java Collections Framework
a. Immutable Collections
With Java 9 and above, you can create immutable collections using factory methods, which means the collection can't be modified after creation. This is useful for read-only data structures, such as configuration files.
java
List<String> fruits = List.of("Apple", "Banana", "Orange");
Set<String> days = Set.of("Monday", "Tuesday");
b. Stream API Integration
Collections integrate beautifully with the Stream API, introduced in Java 8, allowing you to perform operations like filtering, mapping, and reducing in a functional style.
java
List<String> items = Arrays.asList("Apple", "Banana", "Orange");
List<String> result = items.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("A"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(result); // Output: [Apple]
c. Custom Comparators in Sorted Collections
When using sorted collections like TreeSet or TreeMap, you can define custom sorting logic using Comparator.
java
TreeSet<String> sortedSet = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.reverseOrder());
sortedSet.add("Banana");
sortedSet.add("Apple");
sortedSet.add("Orange");
System.out.println(sortedSet); // Output: [Orange, Banana, Apple]
Conclusion
The Java Collections Framework is a powerful tool that every Java developer must master. From basic data structures like lists and sets to advanced features like custom comparators and stream operations, the JCF provides a comprehensive toolkit for handling data. By choosing the right collection type, following best practices, and leveraging advanced features, you can write efficient, scalable, and maintainable code.